With the introduction of Headless CMSs, a lot of companies have started switching from traditional CMSs to more lightweight versions. This shift is very evident in the world of ecommerce where a number of high-profile brands have started using headless CMSs as the base for their online stores. However, some online store owners are not aware that some shopping cart plugins can be used as headless content management systems. In fact, it’s quite possible that some of your favourite ecommerce platforms are already using headless CMSs behind the scenes. In this article, we explore what headless content management systems are and how they work.
What is a Headless CMS?
A headless CMS is a back-end only approach to website development. It doesn’t rely on a user interface or traditional CMS front-end tools to manage content. Instead, it provides an API for developers to build flexible, dynamic web applications that can interact with data stored in the CMS’s database. A headless CMS may include a web interface for managing other aspects of the site, such as users and permissions, but this is a secondary feature and not a replacement for the API.
The term “headless” refers to the separation of content from presentation. When you use a traditional CMS, you create pages by building files with tags that correspond to the elements on those pages. In short, you describe how your content should be presented to visitors. In a headless CMS, you simply store those pages as data in the CMS’s database. It’s then up to you to interpret that data and present it in whatever way makes sense for your application or website.
A headless CMS has three parts:
- A storage layer
- A web service or API for accessing content
- An application server or web browser.
The storage layer holds all the content. In a traditional CMS, this is a database. In a headless CMS it can be any data store, from files on disk to NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Redis to remote services like Amazon S3.
The web service or API exposes that content to the application server or web browser. This provides a standard way for the front end to get at the content.
The application server takes that content and displays it to users via HTML, JavaScript and CSS files. And while it’s possible for developers to do everything from the command line, the usual approach is to use frameworks such as React, Angular or Vue.
The pros and cons of a headless CMS
A headless CMS is a great option if you’re looking for an out-of-the-box workflow that will free you from the restraints of a traditional content management system. In a nutshell, a headless CMS is an application that allows you to store and manage your data in a database, use a well-established programming language to interact with your data, and render your content through a user interface.
A headless CMS allows you to develop your front-end application (UI) with any framework/library you want without the need to install any more components on your server.
In a typical CMS, content is stored in a database and delivered to the front-end application via a web service. In a headless CMS the content is delivered directly from a storage layer to an application server or web browser. The headless approach offers many advantages for developers and businesses, but there are some gotchas that lead organisations to choose traditional CMS architectures instead.
Advantages There are four main reasons why companies choose to use headless CMS:
1. Access to Content
Using an API gives you full access to all content within the CMS. You can change, update or delete any content within the system, enabling you to fully control your content and data.
2. Faster Development
A headless CMS allows developers to build applications with ease. This means that development teams can work on new features and functionality much quicker than if they were using a traditional CMS.
3. Scalability
Since there is no front-end interface, building websites becomes much faster as developers do not have to worry about creating multiple versions of their site for various devices. This also makes it easier to scale up.
4. Faster Page Loads
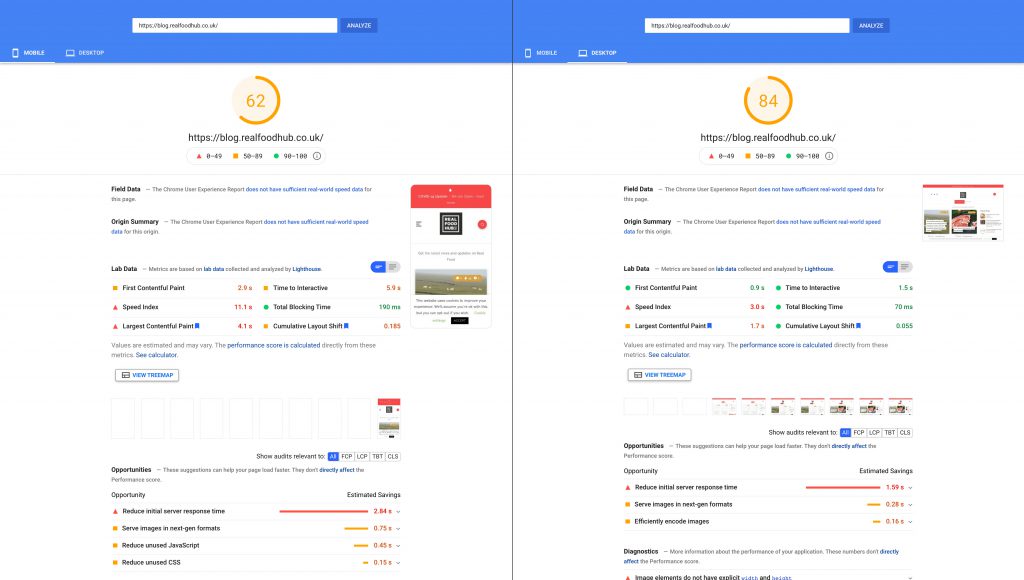
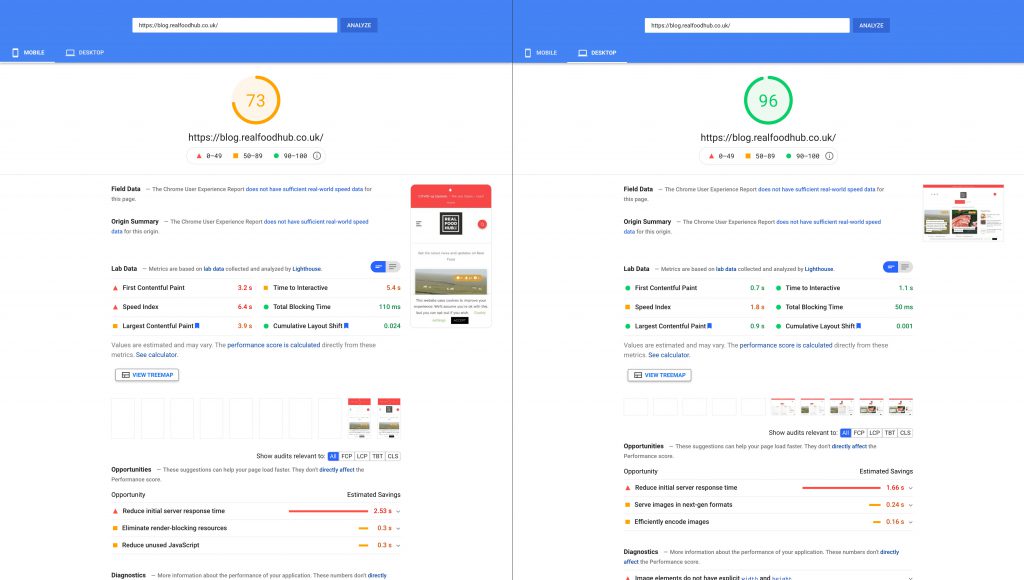
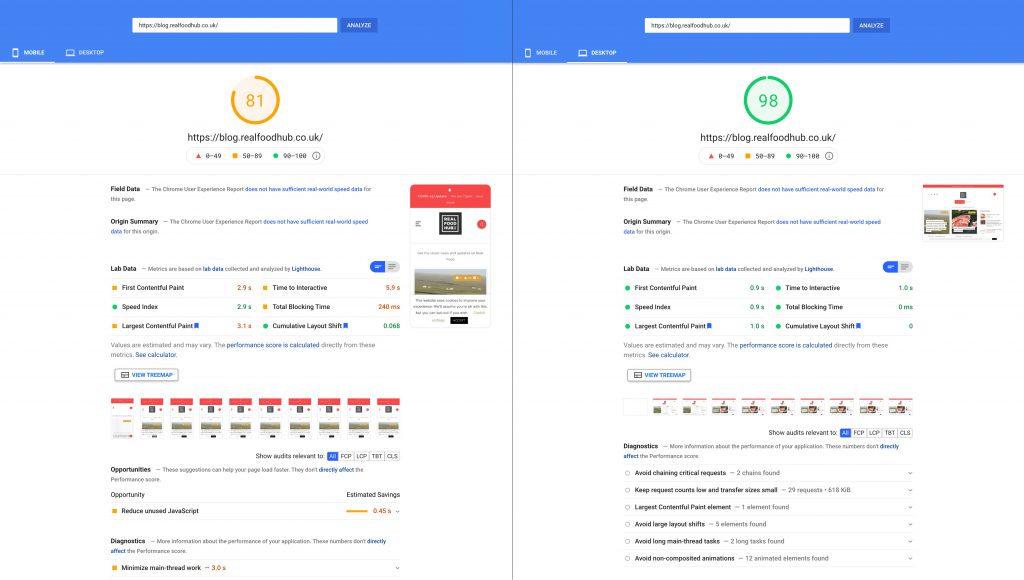
With headless CMS, the data is stored on the back end of your website so that only the front end needs to retrieve it each time it needs to load a page or post. This means that pages load faster which translates into happier visitors and higher search engine rankings.
Disadvantages
- A content management system that is not integrated into the front end can be difficult to manage and edit by designers and nontechnical users.
- The API can be cumbersome to work with and does not lend itself to quick edits. Some developers believe that there is no need for a separate API and prefer the simplicity of editing the same files as both back end and front end scripts.
- Headless content management systems often sacrifice design for functionality by not providing an interface for designing pages and sections of pages. It will require a Designer/Developer on hand for bespoke templates and design changes.
Conclusion
Headless CMS’s can provide more features than traditional CMS. It’s also much more scalable and secure. It’s also much easier to distribute the same content via multiple platforms, whether that may be an App, or across other media platforms.
If you require a similar solution please Contact Us.